Setup
Since version 2.6, Netpicker supports file transfer configuration backups using various protocols like SCP, SFTP and TFTP. To enable this, you need configure and start up an extra container called ‘transferium’ using the options/transferium.yml docker compose file:
https://github.com/netpicker/netpicker/blob/main/options/transferium.yml
docker compose -f docker-compose.yml -f options/transferium.yml up -d
Also, in Admin -> Settings you need to set an environment variable SHENV_JUMP_HOST to the host IP address of the Netpicker machine.
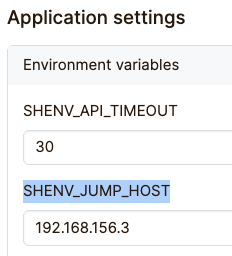
File transfer configuration
The file transfer YAML file describes the steps to obtain and transfer information from a network device to be stored in the Netpickers configs git repository. The information can be anything, although the main purpose is to collect the configuration itself.
The root element of the yaml is the protocols key with names of individual protocols, and should contain at least the default key.
Any given protocol can have:
initial_context: object to initialize (local) variables used to define in the following objects.The following variables are present in any given moment:dst_ipdst_filedst_volumeusernamepasswordsecret
initialize: array of commands to obtain the information and store it in the appropriate filefinalize: array of commands to clean up (temporary files etc)errors: objects defining what exception to raise in case of a matching reply from the devicetransfers: an object of transfer name (i.e. scp, sftp) with an array of commands that define how to transfer information to Netpicker. The transfers are executed in the defined order one by one until the {dst_file} is created so that it can be consumed by the Netpicker API.
Here is a transfer example of sftp for f5_linux device:
sftp: # the name is arbitrary but should be descriptive enough
- command: sftp {username}@{dst_ip} # the first command to be send
finally: # execute this command at the end even in case of failure
command: "bye" # the command
method: send_command # what netmiko method to use
kwargs: # additional keyword arguments to issue with the method
expect_string: '#'
prompts: # the reply from the command is being matched against these keys
password: "{password}" # if password appeared -> emit the password
onnected to: # if C/connected to -> issue the put command
command: put {src_file} {dst_file}
method: send_command
kwargs:
expect_string: "sftp>"
read_timeout: 600For devices that do not support any advanced file transfer, one can use a screen scraping command like this:
screen:
- show-run: tmsh show running-config recursiveThe show-run is a shortcut for
- command: tmsh show running-config recursive
method: save_command_output
kwargs:
filename: {dst_file}The save_command_output is not a netmiko native method but as the name suggest it takes the cli response of the device and saves it under the filename.
To avoid repetitiveness, one should use anchors. If there is more than one protocol, but the protocols have similar transfer methodology, one can use inheritance like:
protocols:
default:
initial_context:
src_file: /var/local/scf/exportedconfig
initialize:
- command: tmsh show running-config recursive > {src_file}
...
ucs:
extends: default
overrides:
initial_context:
src_file: /var/local/ncm.ucs
initialize:
- command: tmsh save /sys ucs {src_file}In here, the ucs protocol will use the same steps as the default protocol but with overridden initial_context and initialize block.
